IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identity is an unique number provided to every GSM, CDMA and other phones for unique identification globally. The IMEI number is used usually used to identify the device and also can be used to report stolen or lost phones by the owners to the Network Operator. This allows for the Network operators to disallow service to that device and misuse the device.
A IMEI number can normally be retrieved by calling “*#06#” which displays IMEI number of the device. Most smart phones like Android and iPhone display this in their Settings section.
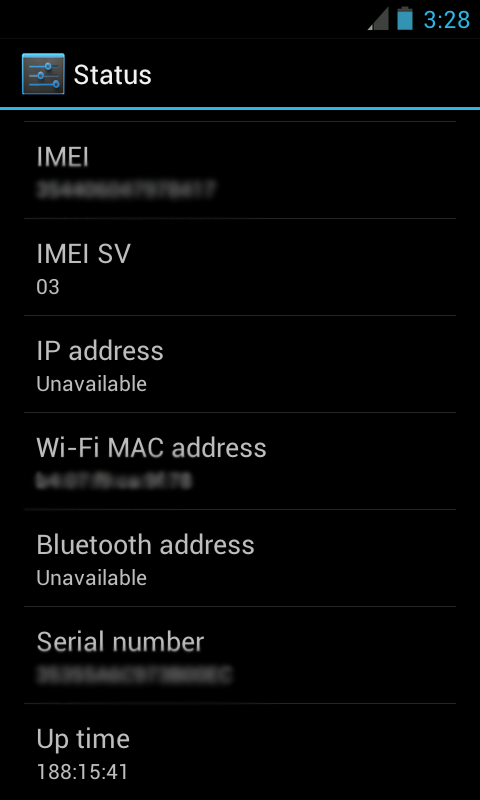
Specifically for Android:
System Settings >> About Phone >> Status >>IMEI
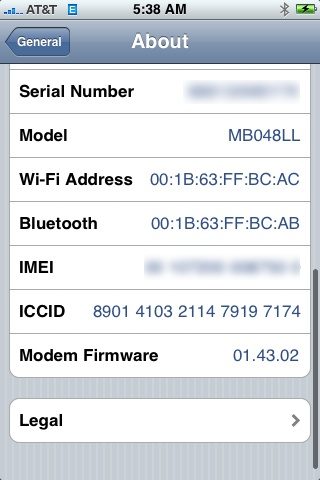
For iPhone:
Settings >> General: About tab >> IMEI
The IMEI (14 decimal digits plus a check digit) or IMEISV (16 digits) includes information on the origin, model, and serial number of the device. The structure of the IMEI/SV are specified in 3GPP TS 23.003. The model and origin comprise the initial 8-digit portion of the IMEI/SV, known as the Type Allocation Code (TAC). The remainder of the IMEI is manufacturer-defined, with a Luhn check digit at the end. For the IMEI format prior to 2003, the GSMA guideline was to have this Check Digit always transmitted to the network as zero. This guideline seems to have disappeared for the format valid from 2003 and onwards.
As of 2004, the format of the IMEI is AA-BBBBBB-CCCCCC-D, although it may not always be displayed this way. The IMEISV drops the Luhn check digit in favour of an additional two digits for the Software Version Number (SVN), making the format AA-BBBBBB-CCCCCC-EE
| AA | – | BB | BB | BB | – | CC | CC | CC | D or EE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Old IMEI | TAC | FAC | Serial number | (Optional) Luhn checksum | ||||||
| New IMEI | TAC | |||||||||
| Old IMEISV | TAC | FAC | Software Version Number (SVN). | |||||||
| New IMEISV | TAC | |||||||||